- Acne
- Actinic Keratosis
- Aesthetics
- Alopecia
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Buy-and-Bill
- COVID-19
- Case-Based Roundtable
- Chronic Hand Eczema
- Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
- Drug Watch
- Eczema
- General Dermatology
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Melasma
- NP and PA
- Pediatric Dermatology
- Pigmentary Disorders
- Practice Management
- Precision Medicine and Biologics
- Prurigo Nodularis
- Psoriasis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Rare Disease
- Rosacea
- Skin Cancer
- Vitiligo
- Wound Care
Article
1 in 5 With Spontaneous Urticaria Has Celiac Disease Autoantigen Expression
Author(s):
Researchers said expression of the autoantigen was increased in patients.
1 in 5 patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) has an increased expression of tissue transglutaminase 2 (TG2), or the autoantigen involved in celiac disease.
kanachaifoto/AdobeStock
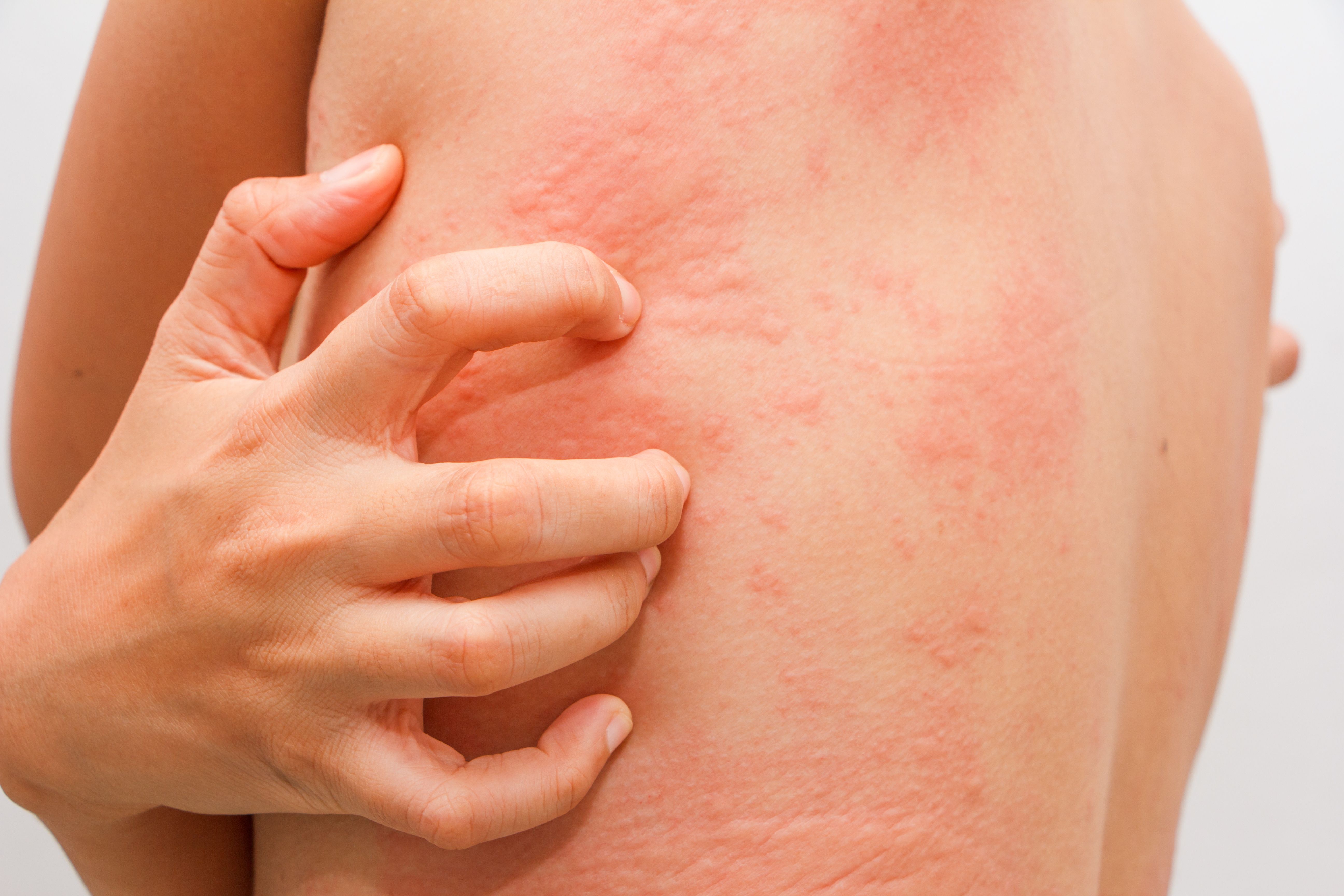
In a recent assessment,1 researchers sought to determine potential correlations between IgE antibodies and several autoantigens.
In type I autoimmune CSU, or autoallergic CSU, autoantigens such as thyroperoxidase (TPO) and interleukin 24 (IL-24), drive signs and symptoms of disease. Prior research2 has shown that TG2 is not only increased in CSU patients and their lesioned skin mast cells, but it has also been thought to be a severity biomarker.
Using human IgE capture ELISA, researchers assessed and quantified IgE levels correlated with and directed against autoantigen TG2 (IgE-anti-TG2). Furthermore, they examined both clinical and serological features of CSU.
Participants (n=214) either had CSU (n=160) or were deemed clinically healthy (n=54) and assigned to a control group. Researchers then collected demographic and disease-specific data for each participant, including sex, age, disease duration, angioedema presence, positive skin prick tests to inhalant allergens, and blood basophil and eosinophil counts.
They also quantified the results of participants’ autologous skin tests, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) results, erythrocyte sedimentation rates, urticarial activity scores, and urticariacontrol test results.
Following their analysis, researchers noted that 127 participants with CSU were IgE-anti-TG2 negative and 33 were IgE-anti-TG2 positive.
20.6% of participants with CSU had elevated IgE-anti-TG2 levels, and in general, participants with CSU had significantly higher levels of IgE-anti-TG2 serum than that of their healthy, control group participant counterparts.
“Additional studies are needed to compare levels of IgE-anti-TG2 in different responders to omalizumab (fast, slow, non-responders) both at baseline and during follow-up,” assessment authors wrote. “Finally, CSU patients are shown to have an increased risk of celiac disease and vice versa, and further studies should clarify whether the presence of IgE-anti-TG2 is associated with this risk.”
References
- Su H, Kolkhir P, Scheffel J, et al. One in five patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria has IgEto tissue transglutaminase 2. Allergy. 2023. doi:10.1111/all.15734
- Hong GU, Ro JY, Bae Y, et al. Association of TG2 from mast cells and chronic spontaneous urticaria pathogenesis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016;117:290-297. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2016.06.026
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.











