- Acne
- Actinic Keratosis
- Aesthetics
- Alopecia
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Buy-and-Bill
- COVID-19
- Case-Based Roundtable
- Chronic Hand Eczema
- Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
- Drug Watch
- Eczema
- General Dermatology
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Melasma
- NP and PA
- Pediatric Dermatology
- Pigmentary Disorders
- Practice Management
- Precision Medicine and Biologics
- Prurigo Nodularis
- Psoriasis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Rare Disease
- Rosacea
- Skin Cancer
- Vitiligo
- Wound Care
News
Article
High Levels of Cholesterol, Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol, Among Genetic Risk Factors for Psoriasis
Author(s):
Investigators explored the genetic relationship between psoriatic disease and serum lipid levels.
pimentos/Adobe Stock
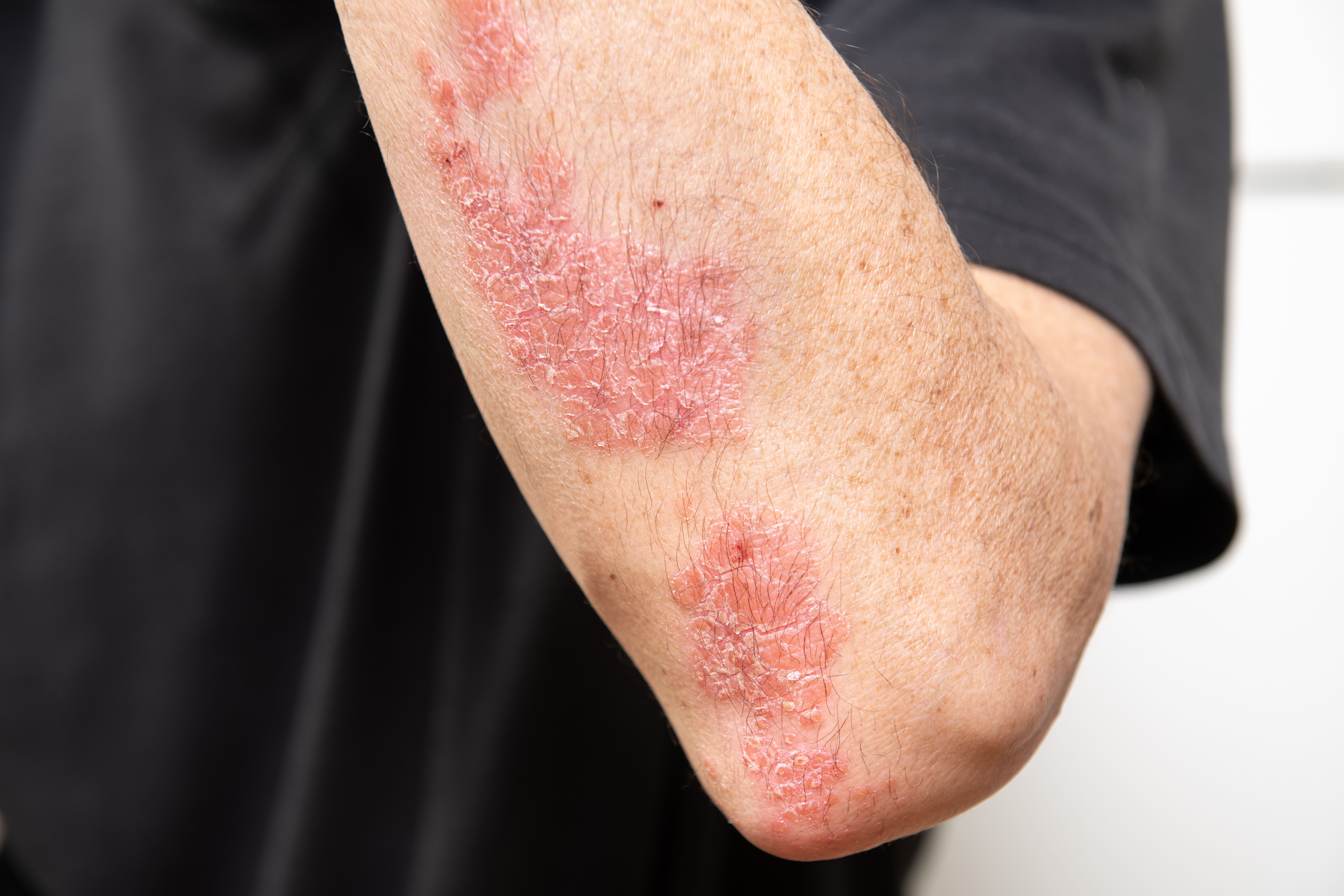
A recent 2-way Mendelian randomization (MR) study aimed to explore the causality between lipid metabolism and psoriasis, finding that psoriasis and total cholesterol, total free cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels, among others, share a genetically causal relationship with one another.
Additionally, they found that high levels of cholesterol, total free cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol, are considered genetic risk factors for psoriatic disease.
Previous studies, study authors wrote, have hinted at abnormal lipid metabolism in psoriasis patients, with elevated serum cholesterol levels and lipid disorders being prevalent. A previous clinical study with 35,000 participants suggested a significant association between metabolic syndrome and an increased risk of psoriasis. This led study authors to explore the genetic relationship between lipid metabolism and psoriasis.
The study employed genetic variants associated with lipid exposure, utilizing data from 12 lipid-related genome-wide association studies (GWASs) as exposure factors and psoriasis as the outcome.
The study revealed findings through both forward and reverse causal effect analyses. In the forward causal effect, abnormalities in lipid metabolism, particularly total cholesterol, total free cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and specific cholesterol ester levels, were identified as contributing factors to the development of psoriasis. This reinforced the hypothesis that disordered lipid metabolism may play a crucial role in promoting psoriasis, supported by both clinical and animal experimentation.
Conversely, the reverse causal effect analysis, where psoriasis was considered the exposure, showed no evidence of psoriasis promoting abnormal alterations in lipid metabolism at the genetic level. This negates the idea that psoriasis itself leads to lipid metabolism disorders and suggests that treating lipid metabolism disorders could be crucial in managing psoriasis.
The study, however, had several limitations, as noted by study authors. The study did not account for cross-generational effects, and the reliance on GWAS data primarily from European populations prompts the need for further investigations across diverse populations.
"To our knowledge, this is the first bidirectional MR study to explore the causality between lipid metabolism disorders and psoriasis," study authors wrote. "Our study found genetic causality between psoriasis and total cholesterol, total free cholesterol, LDL cholesterol levels, cholesterol ester levels in large VLDL, cholesterol ester levels in medium LDL and no evidence of concurrent reverse causality."
Reference
Zhou Q, Jin X, Li H, et al. Cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein as a cause of psoriasis: Results from bidirectional Mendelian randomization. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. Published online November 29, 2023. doi:10.1111/jdv.19670
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.







