- Acne
- Actinic Keratosis
- Aesthetics
- Alopecia
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Buy-and-Bill
- COVID-19
- Case-Based Roundtable
- Chronic Hand Eczema
- Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
- Drug Watch
- Eczema
- General Dermatology
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Melasma
- NP and PA
- Pediatric Dermatology
- Pigmentary Disorders
- Practice Management
- Precision Medicine and Biologics
- Prurigo Nodularis
- Psoriasis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Rare Disease
- Rosacea
- Skin Cancer
- Vitiligo
- Wound Care
News
Article
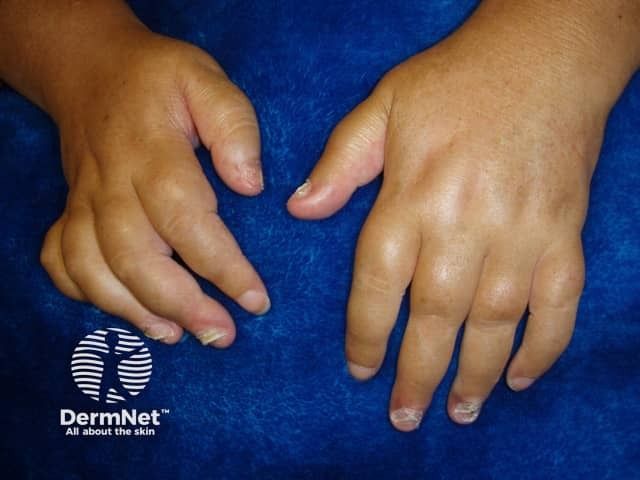
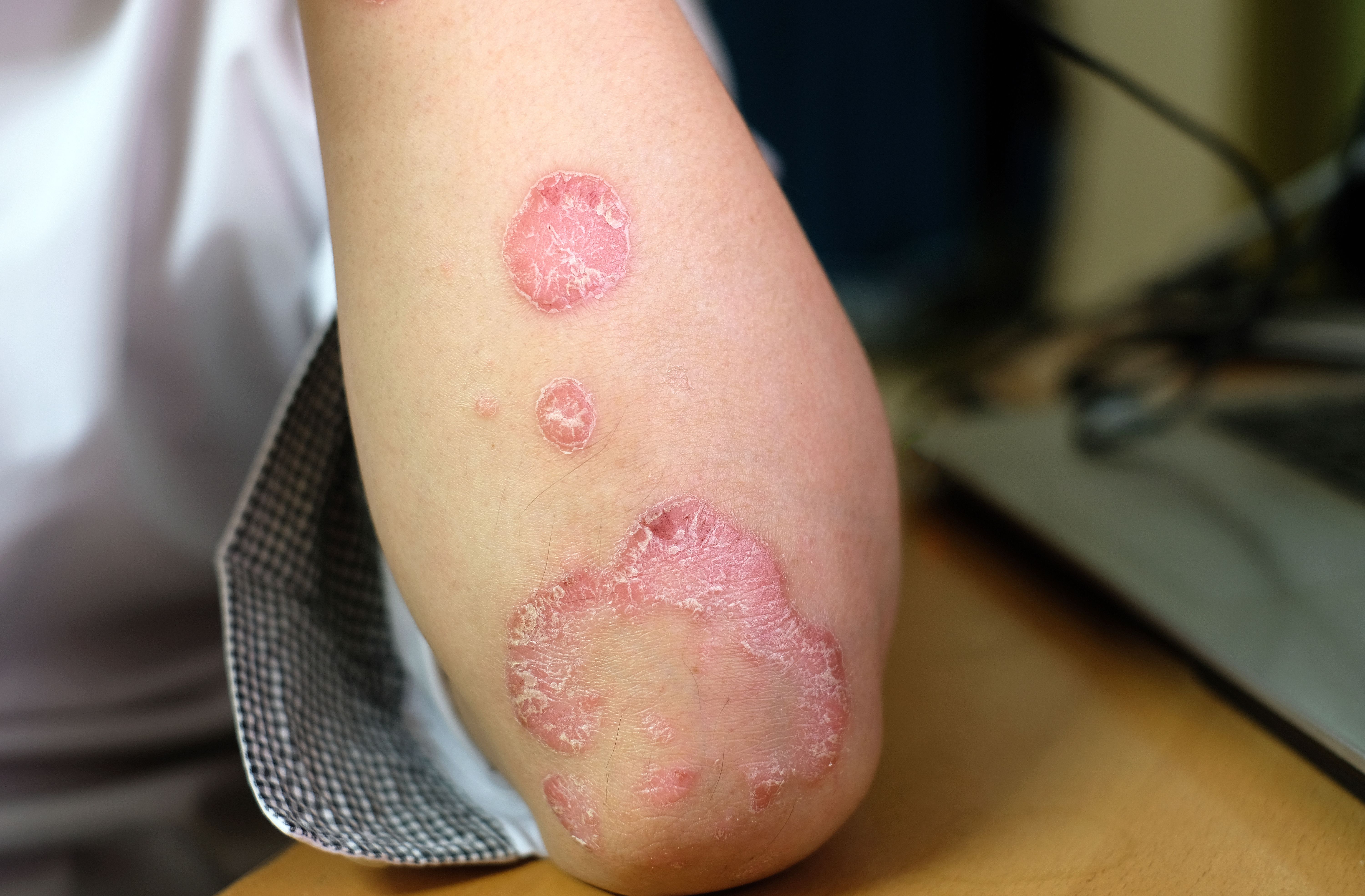
Phase 3 Trials Confirm Deucravacitinib’s Efficacy in PsA
Author(s):
Key Takeaways
- Deucravacitinib showed significant efficacy in PsA, achieving primary and secondary endpoints in phase 3 trials.
- The trials involved over 1,400 patients, including bDMARD-naïve and TNFα inhibitor-experienced individuals.
Deucravacitinib achieved ACR20 response in patients with PsA at week 16, with a safety profile consistent with previous studies.
This week, Bristol Myers Squibb announced positive outcomes from 2 pivotal phase 3 trials, POETYK PsA-1 (NCT04908202) and POETYK PsA-2 (NCT04908189), evaluating the efficacy and safety of deucravacitinib (Sotyktu) in adults with active PsA. These randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials involved over 1,400 patients across both studies. Participants were either biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD)-naïve or had prior exposure to TNFα inhibitors.1
"[PsA] is a heterogenous disease that causes a range of different symptoms, including joint pain and swelling, as well as psoriatic skin lesions. Despite available therapies, rheumatologists continue to express a need for a safe and effective oral treatment," said Roland Chen, MD, senior vice president and head, Immunology, Cardiovascular and Neuroscience development, Bristol Myers Squibb, in a news release. "These POETYK PsA-1 and POETYK PsA-2 findings demonstrate that oral [deucravacitinib] has the potential to be the first TYK2 inhibitor for people living with [PsA] and reinforce the established efficacy and safety profile of [deucravacitinib]. We are encouraged by the positive data across both phase 3 trials and look forward to discussing the results with health authorities."
Key Findings
Both trials achieved their primary endpoint, demonstrating that a significantly higher proportion of patients treated with deucravacitinib achieved an ACR20 response, defined as at least a 20% improvement in PsA signs and symptoms, by week 16 compared to those receiving placebo. Secondary endpoints were also met, with improvements observed across key measures of PsA disease activity at week 16. The company stated the safety profile of deucravacitinib was consistent with prior findings from phase 2 PsA and phase 3 moderate to severe plaque psoriasis clinical trials.
Study Design
The POETYK PsA-1 trial enrolled approximately 670 patients with active PsA who had not been previously treated with bDMARDs. The POETYK PsA-2 trial enrolled approximately 730 patients with active PsA, including both bDMARD-naïve patients and those who had previously received TNFα inhibitor treatment. Additionally, the POETYK PsA-2 trial included a safety reference arm using apremilast.
Both trials featured a 52-week treatment period. This included a placebo-controlled phase up to week 16, after which patients were reallocated to active treatment for the remainder of the study. The company stated patients who completed the trials were given the opportunity to enroll in an open-label extension study.
Mechanism of Action
According to Bristol Myers Squibb, deucravacitinib is an oral, first-in-class selective tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor designed to modulate key cytokines implicated in immune-mediated diseases, including interleukin-23 (IL-23), interleukin-12 (IL-12), and Type 1 interferons. It achieves its selectivity through allosteric inhibition by targeting the regulatory domain of TYK2, rather than directly inhibiting JAK1, JAK2, or JAK3 at therapeutic doses. Researchers stated this distinct mechanism of action represents a new class of treatment in the management of immune-mediated diseases.
Implications
The company wrote that POETYK PsA trial results demonstrate that deucravacitinib has the potential to become the first TYK2 inhibitor for PsA, addressing a significant unmet need for effective oral therapies. The findings also reinforce deucravacitinib’s established efficacy and safety profile, as observed in prior trials for other immune-mediated diseases, such as moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.2 Bristol Myers Squibb stated it plans to present detailed data from these trials at upcoming medical congresses and engage with regulatory authorities to discuss the results.
Conclusion
Researchers found deucravacitinib represents a promising new therapeutic option for patients with PsA, offering a novel mechanism of action and a favorable efficacy and safety profile. These findings underscore the potential of TYK2 inhibitors to transform the management of immune-mediated diseases.
References
- Bristol Myers Squibb announces positive topline results from two pivotal phase 3 trials evaluating Sotyktu (deucravacitinib) in adults with psoriatic arthritis. News Release. BuisnessWire. Published December 23, 2024. Accessed December 24, 2024. https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20241220275848/en/Bristol-Myers-Squibb-Announces-Positive-Topline-Results-from-Two-Pivotal-Phase-3-Trials-Evaluating-Sotyktu-deucravacitinib-in-Adults-with-Psoriatic-Arthritis
- Armstrong AW, Gooderham M, Warren RB, et al. Deucravacitinib versus placebo and apremilast in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: Efficacy and safety results from the 52-week, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase 3 POETYK PSO-1 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88(1):29-39. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.07.002
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.