- Acne
- Actinic Keratosis
- Aesthetics
- Alopecia
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Buy-and-Bill
- COVID-19
- Case-Based Roundtable
- Chronic Hand Eczema
- Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
- Drug Watch
- Eczema
- General Dermatology
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Melasma
- NP and PA
- Pediatric Dermatology
- Pigmentary Disorders
- Practice Management
- Precision Medicine and Biologics
- Prurigo Nodularis
- Psoriasis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Rare Disease
- Rosacea
- Skin Cancer
- Vitiligo
- Wound Care
Publication
Article
Dermatology Times
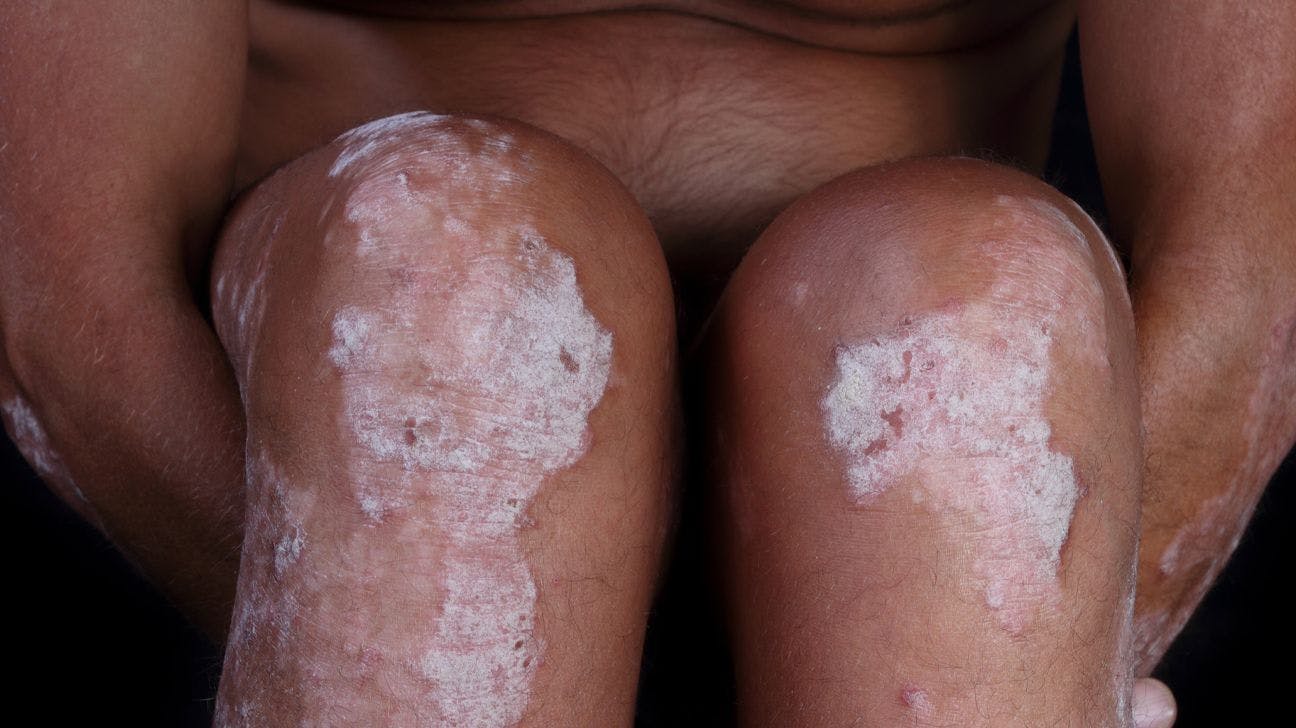
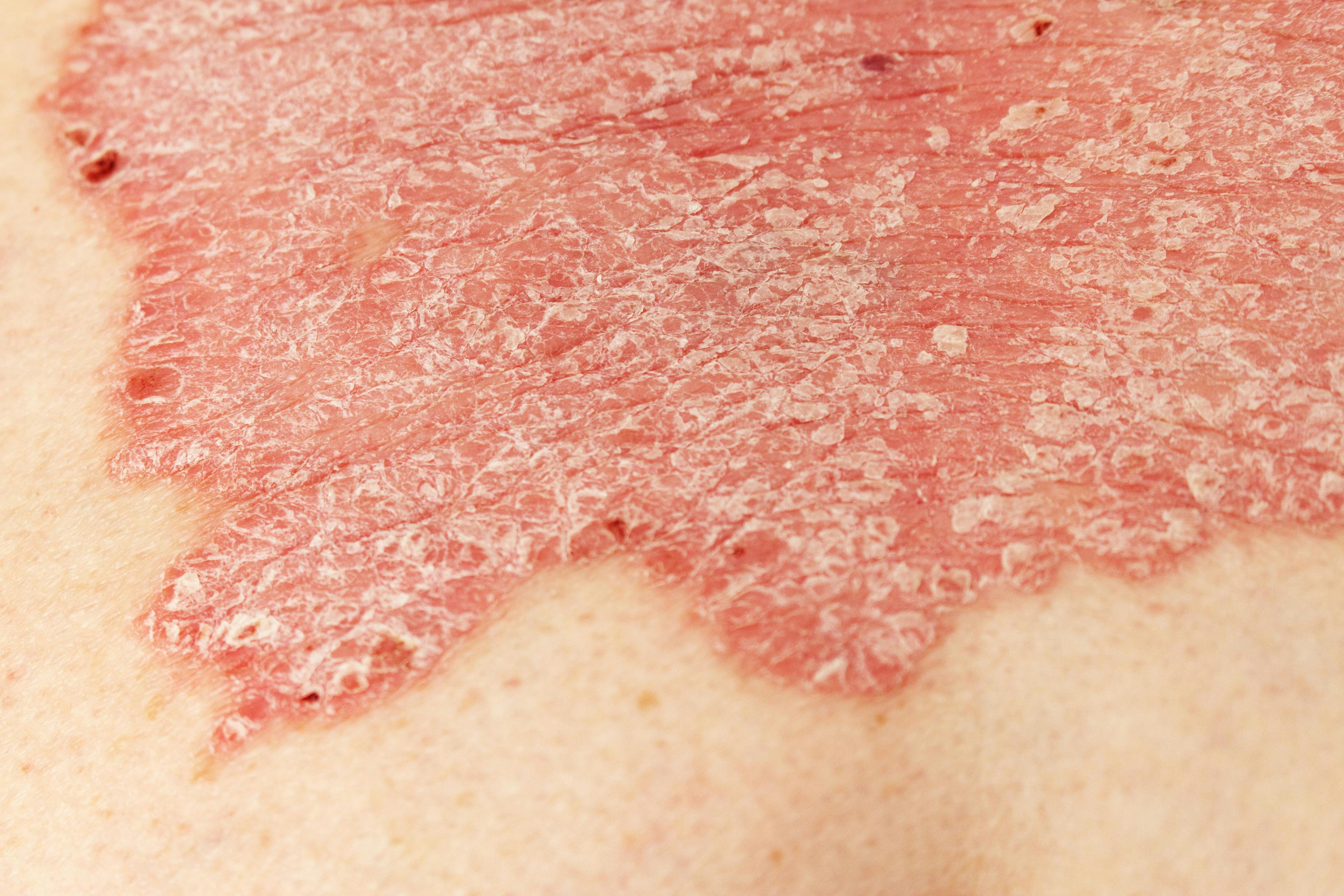
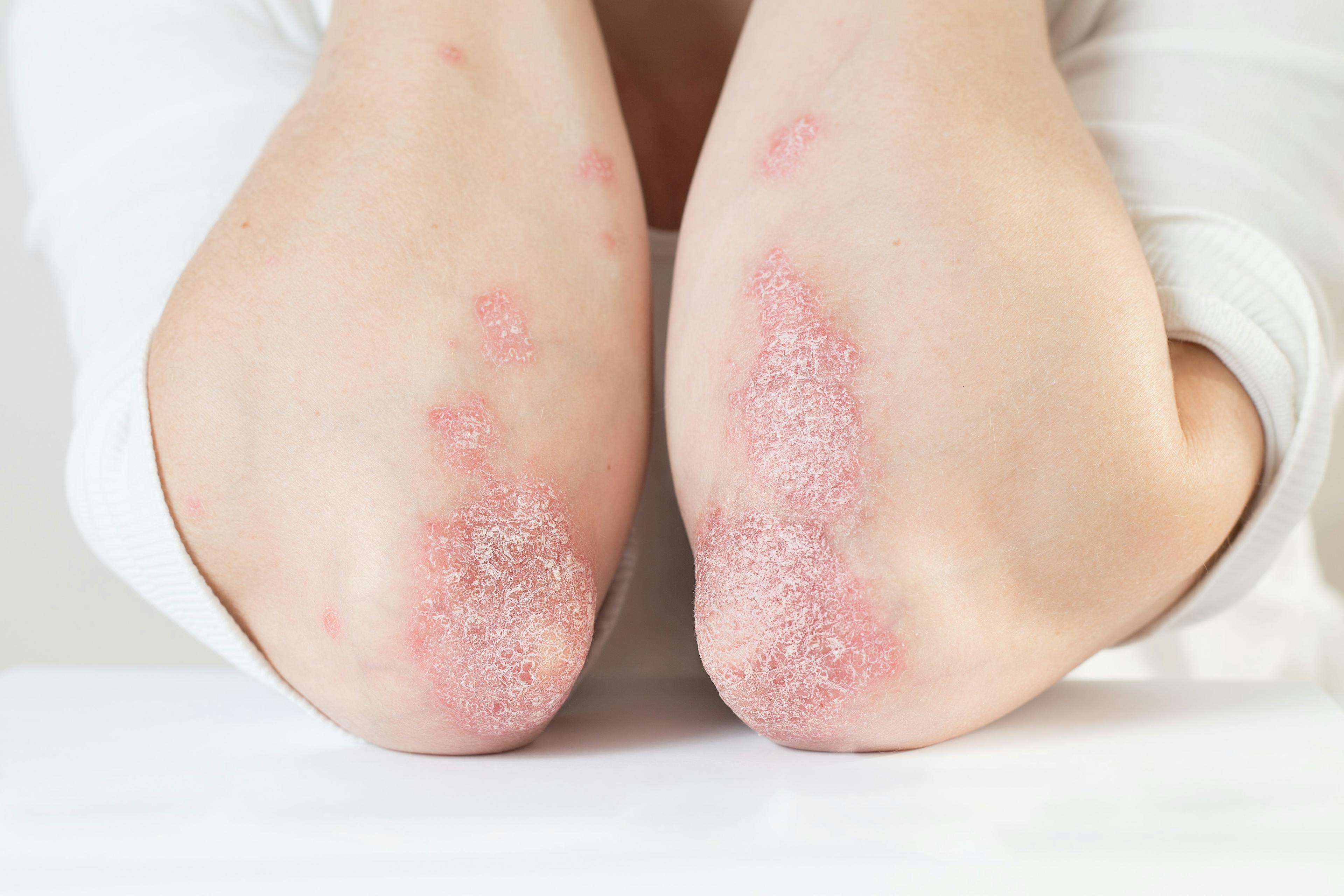
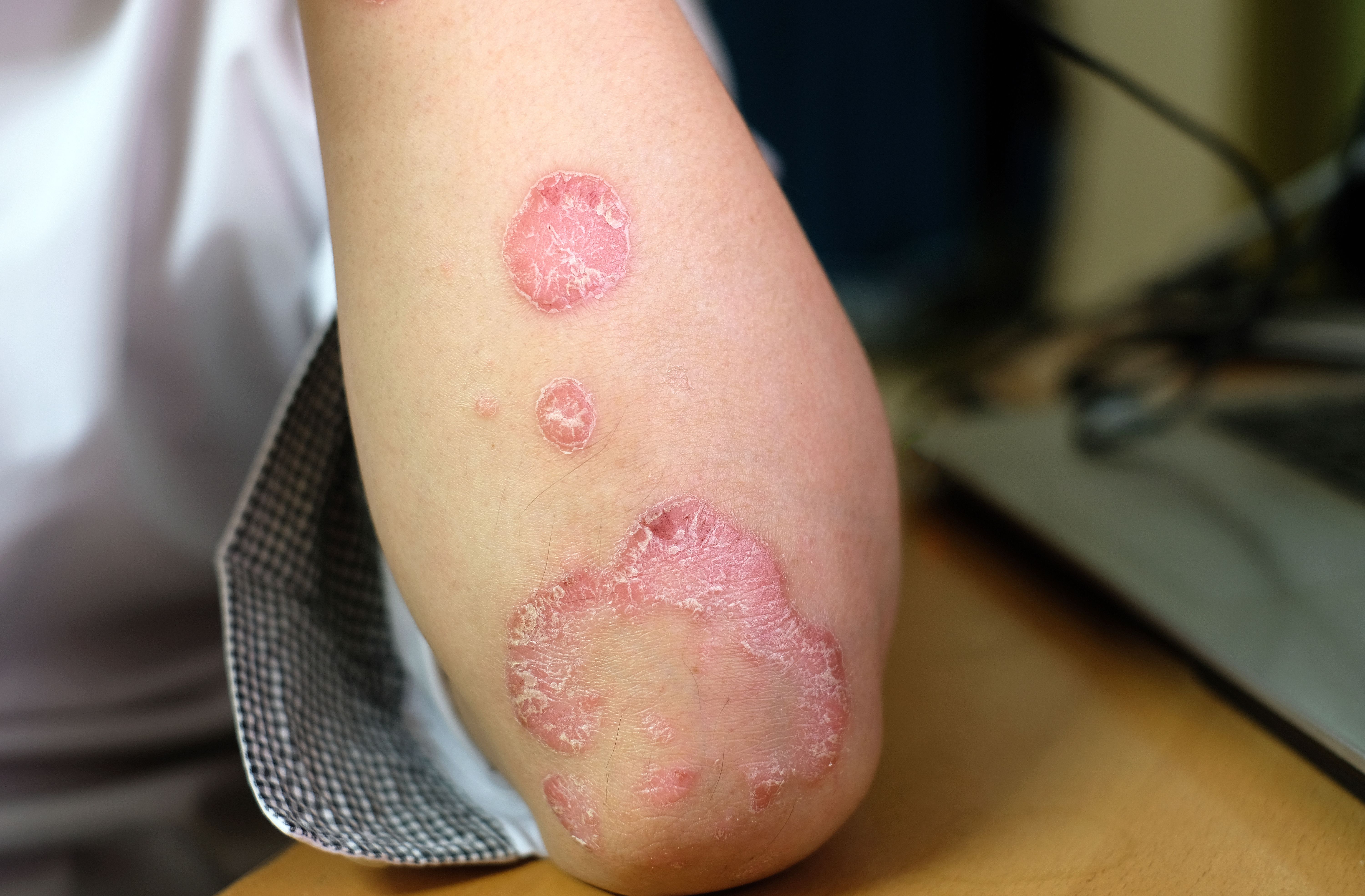
3 Dietary Considerations for Psoriasis
Author(s):
Whitney Linsenmeyer, PhD, RD, LD, provides 3 dietary considerations for patients with psoriasis.
Whitney Linsenmeyer, PhD, RD, LD, an assistant professor of nutrition at Saint Louis University Doisy College of Health Sciences and spokesperson for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, says:
1. An anti-inflammatory diet may be a useful strategy in managing psoriasis.
The Mediterranean diet is a sound place to start; this approach is endorsed by leading health organizations, including the World Health Organization and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. The Mediterranean diet is rich in vegetables, fruits, nuts and seeds, whole grains, fish, and healthy oils. Dietary recommendations include 1) core foods to enjoy daily, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, beans, herbs, spices, and nuts, and healthy fats such as olive oil; 2) fish and seafood at least twice weekly; 3) moderate portions of dairy, eggs, and occasional poultry; and 4) infrequent servings of red meat and sweets.
2. Specific anti-inflammatory foods include:
- Green leafy vegetables, such as spinach, kale, and collards
- Fruit, including strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, cherries, oranges, and apples
- Nuts, such as almonds, walnuts, and pistachios
- Fatty fish, including salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines
- Tomatoes
- Olive oil
3. For those managing psoriasis, avoiding specific foods that are known triggers or may worsen symptoms (ie, gluten in wheat, rye, barley) is vital.

Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.